Using Log File Analysis for Crawl Budget Optimization
Among the most powerful yet often underutilized techniques in an SEO professional's toolkit is log file analysis for crawl budget optimization. This...
%20(1)-2.png)
Let’s talk about small vs. large website SEO.
When working on technical SEO, the size of the website plays a major role in the strategy. Working with thousands of pages requires different skills related to automating sitemap creation and updates, preventing duplicate content, and more. This post focuses on managing crawl budget, an important area that distinguishes small-site SEO from large-site SEO.
Before we go too much further, let’s define crawl budget. This term is thrown around in SEO, often without having a firm understanding of the concept. Basically, it refers to the number of pages that Google can crawl and index from a website in a certain period of time. Some might be surprised to find that Google does not necessarily crawl all of a website’s pages, even if they are listed in the sitemaps.
Therefore, if a company isn’t working on optimizing its website’s crawl budget, having a bigger website isn’t always better.
So, if you host a large website with hundreds of thousands of pages, how can you be sure that Google is picking up all the content and indexing it? The good news is that marketing professionals can influence a site’s crawl budget by employing strong SEO practices.
This guide focuses on the two main elements determining crawl budget - crawl capacity limit and crawl demand.
Essentially, the crawl demand is what Google wants to crawl based on the size of the site, how often it is updated, content quality, and relevance compared to competitors in the industry. By consistently updating content to prevent staleness, companies can increase crawl demand. In addition, eliminating duplicate content helps increase crawl demand by limiting low-quality URLs.
Finally, following XML sitemap best practices improves crawl demand by keeping pages organized. This differs for large and small websites. For example, a large site that has multiple subdirectories should use a sitemap index, whereas a smaller website might be fine without an index.
According to Google developers, the crawl capacity limit is “the maximum number of simultaneous parallel connections that Googlebot can use to crawl a site, as well as the time delay between fetches…without overloading your servers.”
Since this limit is directly related to page load time and site speed, focusing on Core Web Vitals is key for increasing a website’s crawl capacity limit. The Google Search Console Core Web Vitals report is one tool to manage these site statistics. The three major metrics are the largest contentful paint (LCP), first input delay (FID), and cumulative layout shift (CLS). Without going too deep into the technical jargon, there are suggested performance ranges (displayed below) for the three metrics that can guide a company’s technical SEO strategy.
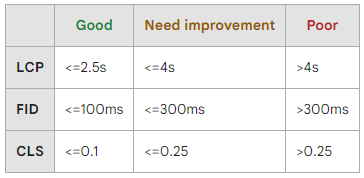
Source: Google Core Web Vitals Report
Moz offers a comprehensive guide to page speed, including steps to take to speed up your website. To summarize the key points, they identified the following actionable steps:
By following these steps, companies can work toward a page speed goal that will optimize crawl budget.
Unfortunately, many business leaders don’t know if they’re optimizing their website’s crawl budget. Without digging into a lot of the data in GSC and seeing how many pages are crawled and indexed vs. how many are not, it’s difficult to identify crawl budget issues.
At Hire a Writer, we conduct regular sit audits for our clients to ensure that we identify and rectify technical SEO issues as soon as possible. Our comprehensive SEO audits are never 100% automated - there is always a skilled SEO analyst completing and reviewing the audits to derive meaningful and actionable insights. Contact HAW today to find out more about working with a trusted SEO agency.

Among the most powerful yet often underutilized techniques in an SEO professional's toolkit is log file analysis for crawl budget optimization. This...
%20(1)-1.png)
Here’s the problem: Pretty much all businesses with websites could benefit from SEO, but not all businesses can afford it. Perhaps surprisingly to...
In the complex world of SEO, every piece of data matters. From keyword research to backlink analysis, we constantly seek insights to help us optimize...